- Npm In Visual Studio
- Npm In Visual Studio Code
- How To Run Npm In Visual Studio
- Npm In Visual Studio 2015
Node.js is a platform for building fast and scalable server applications using JavaScript. Node.js is the runtime and npm is the Package Manager for Node.js modules.
Visual Studio Code has support for the JavaScript and TypeScript languages out-of-the-box as well as Node.js debugging. However, to run a Node.js application, you will need to install the Node.js runtime on your machine.
To get started in this walkthrough, install Node.js for your platform. The Node Package Manager is included in the Node.js distribution. You'll need to open a new terminal (command prompt) for the node and npm command-line tools to be on your PATH.
To test that you have Node.js installed correctly on your computer, open a new terminal and type node --version and you should see the current Node.js version installed.
Linux: There are specific Node.js packages available for the various flavors of Linux. See Installing Node.js via package manager to find the Node.js package and installation instructions tailored to your version of Linux.
Windows Subsystem for Linux: If you are on Windows, WSL is a great way to do Node.js development. You can run Linux distributions on Windows and install Node.js into the Linux environment. When coupled with the Remote - WSL extension, you get full VS Code editing and debugging support while running in the context of WSL. To learn more, go to Developing in WSL or try the Working in WSL tutorial.
Hello World
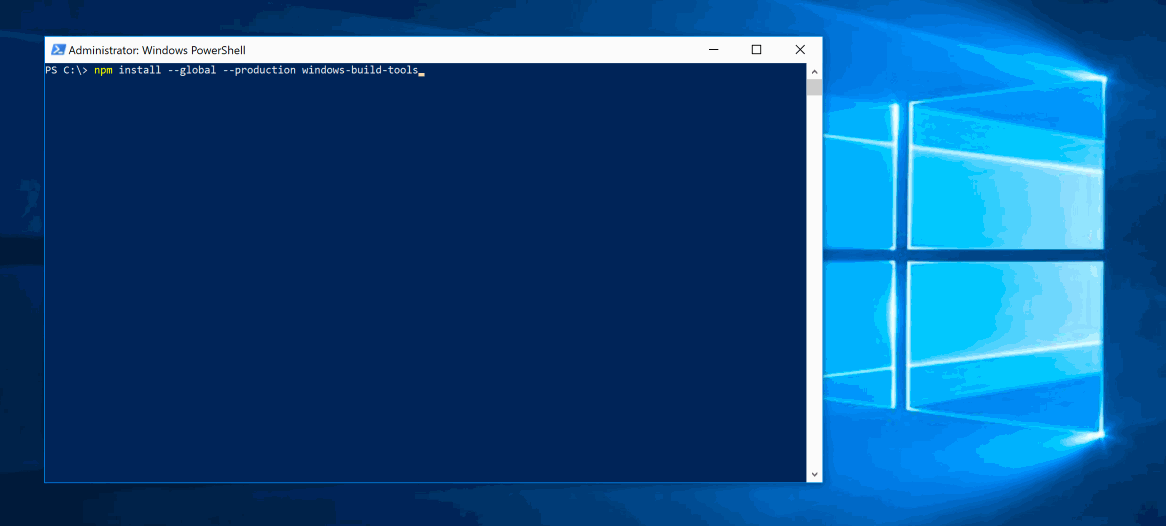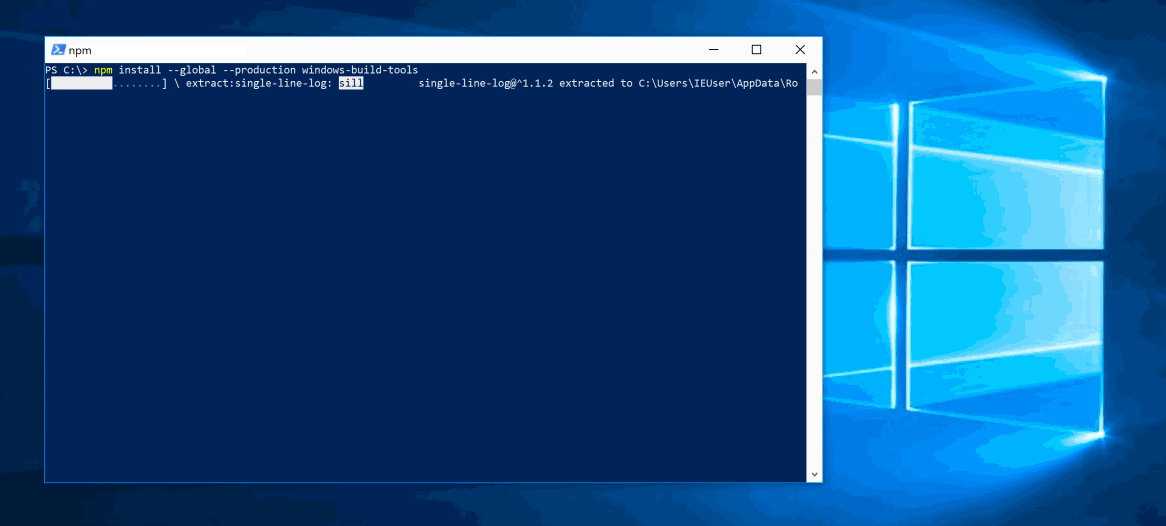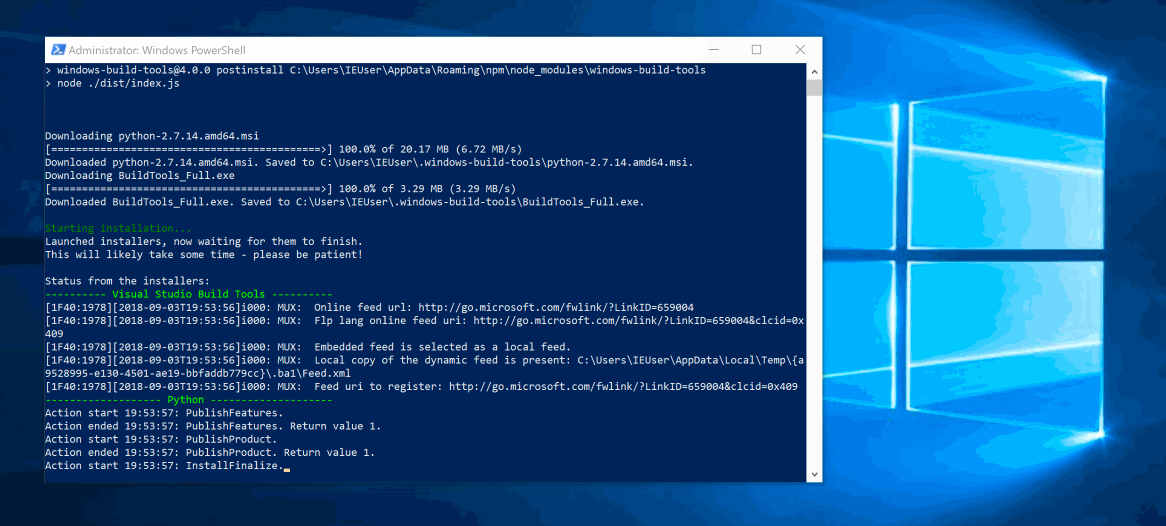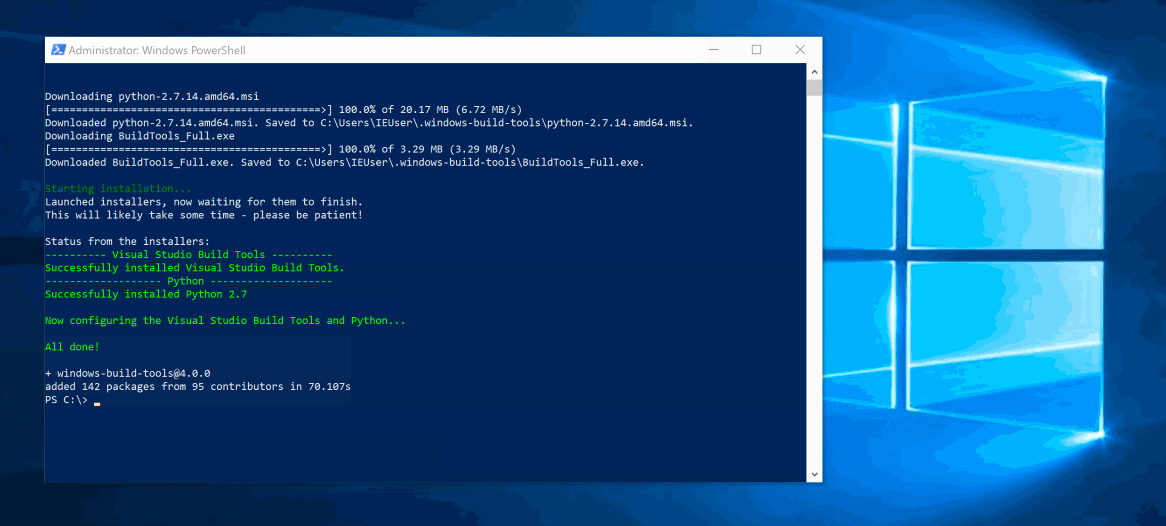
Getting Started with npm in Visual Studio Good Old Command Line. As much as Visual Studio developers love having a UI for their tools, npm is still most easily. The npm Command Line Basics. So you know how to get to the command line quickly from Visual Studio, now what? Go to command line at your SOLUTION directory and execute the following command: 1. You may also use the Visual Studio Package Manager Console: Visual Studio - Tools – NuGet Package Manager - Package Manager Console. The final result will be the following: A nodemodules PER SOLUTION, like NuGet.
Let's get started by creating the simplest Node.js application, 'Hello World'.
Create an empty folder called 'hello', navigate into and open VS Code:
Tip: You can open files or folders directly from the command line. The period '.' refers to the current folder, therefore VS Code will start and open the Hello folder.
From the File Explorer toolbar, press the New File button:
and name the file app.js:
By using the .js file extension, VS Code interprets this file as JavaScript and will evaluate the contents with the JavaScript language service. Refer to the VS Code JavaScript language topic to learn more about JavaScript support.
Create a simple string variable in app.js and send the contents of the string to the console:
Note that when you typed console.IntelliSense on the console object was automatically presented to you.
Also notice that VS Code knows that msg is a string based on the initialization to 'Hello World'. If you type msg. you'll see IntelliSense showing all of the string functions available on msg.
After experimenting with IntelliSense, revert any extra changes from the source code example above and save the file (⌘S (Windows, Linux Ctrl+S)).
Running Hello World
It's simple to run app.js with Node.js. From a terminal, just type:
You should see 'Hello World' output to the terminal and then Node.js returns.
Integrated Terminal
VS Code has an integrated terminal which you can use to run shell commands. You can run Node.js directly from there and avoid switching out of VS Code while running command-line tools.
View > Terminal (⌃` (Windows, Linux Ctrl+`) with the backtick character) will open the integrated terminal and you can run node app.js there:
For this walkthrough, you can use either an external terminal or the VS Code integrated terminal for running the command-line tools.
Debugging Hello World
As mentioned in the introduction, VS Code ships with a debugger for Node.js applications. Let's try debugging our simple Hello World application.
To set a breakpoint in app.js, put the editor cursor on the first line and press F9 or click in the editor left gutter next to the line numbers. A red circle will appear in the gutter.
To start debugging, select the Run View in the Activity Bar:
You can now click Debug toolbar green arrow or press F5 to launch and debug 'Hello World'. Your breakpoint will be hit and you can view and step through the simple application. Notice that VS Code displays a different colored Status Bar to indicate it is in Debug mode and the DEBUG CONSOLE is displayed.
Now that you've seen VS Code in action with 'Hello World', the next section shows using VS Code with a full-stack Node.js web app.
Note: We're done with the 'Hello World' example so navigate out of that folder before you create an Express app. You can delete the 'Hello' folder if you wish as it is not required for the rest of the walkthrough.
An Express application
Express is a very popular application framework for building and running Node.js applications. You can scaffold (create) a new Express application using the Express Generator tool. The Express Generator is shipped as an npm module and installed by using the npm command-line tool npm.
Tip: To test that you've got npm correctly installed on your computer, type npm --help from a terminal and you should see the usage documentation.
Install the Express Generator by running the following from a terminal:
The -g switch installs the Express Generator globally on your machine so you can run it from anywhere.
We can now scaffold a new Express application called myExpressApp by running:
This creates a new folder called myExpressApp with the contents of your application. The --view pug parameters tell the generator to use the pug template engine.
To install all of the application's dependencies (again shipped as npm modules), go to the new folder and execute npm install:
At this point, we should test that our application runs. The generated Express application has a package.json file which includes a start script to run node ./bin/www. This will start the Node.js application running.
From a terminal in the Express application folder, run:
The Node.js web server will start and you can browse to http://localhost:3000 to see the running application.
Great code editing
Close the browser and from a terminal in the myExpressApp folder, stop the Node.js server by pressing CTRL+C.
Now launch VS Code:
Note: If you've been using the VS Code integrated terminal to install the Express generator and scaffold the app, you can open the myExpressApp folder from your running VS Code instance with the File > Open Folder command.
The Node.js and Express documentation does a great job explaining how to build rich applications using the platform and framework. Visual Studio Code will make you more productive in developing these types of applications by providing great code editing and navigation experiences.
Open the file app.js and hover over the Node.js global object __dirname. Notice how VS Code understands that __dirname is a string. Even more interesting, you can get full IntelliSense against the Node.js framework. For example, you can require http and get full IntelliSense against the http class as you type in Visual Studio Code.
VS Code uses TypeScript type declaration (typings) files (for example node.d.ts) to provide metadata to VS Code about the JavaScript based frameworks you are consuming in your application. Type declaration files are written in TypeScript so they can express the data types of parameters and functions, allowing VS Code to provide a rich IntelliSense experience. Thanks to a feature called Automatic Type Acquisition, you do not have to worry about downloading these type declaration files, VS Code will install them automatically for you.
You can also write code that references modules in other files. For example, in app.js we require the ./routes/index module, which exports an Express.Router class. If you bring up IntelliSense on index, you can see the shape of the Router class.
Debug your Express app

You will need to create a debugger configuration file launch.json for your Express application. Click on the Run icon in the Activity Bar and then the Configure gear icon at the top of the Run view to create a default launch.json file. Select the Node.js environment by ensuring that the type property in configurations is set to 'node'. When the file is first created, VS Code will look in package.json for a start script and will use that value as the program (which in this case is '${workspaceFolder}binwww) for the Launch Program configuration.
Save the new file and make sure Launch Program is selected in the configuration dropdown at the top of the Run view. Open app.js and set a breakpoint near the top of the file where the Express app object is created by clicking in the gutter to the left of the line number. Press F5 to start debugging the application. VS Code will start the server in a new terminal and hit the breakpoint we set. From there you can inspect variables, create watches, and step through your code.
Deploy your application
If you'd like to learn how to deploy your web application, check out the Deploying Applications to Azure tutorials where we show how to run your website in Azure.
Next steps
There is much more to explore with Visual Studio Code, please try the following topics:
- Settings - Learn how to customize VS Code for how you like to work.
- Debugging - This is where VS Code really shines.
- Video: Getting started with Node.js debugging - Learn how to attach to a running Node.js process.
- Node.js debugging - Learn more about VS Code's built-in Node.js debugging.
- Debugging recipes - Examples for scenarios like client-side and container debugging.
- Tasks - Running tasks with Gulp, Grunt and Jake. Showing Errors and Warnings.
React is a popular JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building web application user interfaces. The Visual Studio Code editor supports React.js IntelliSense and code navigation out of the box.
Welcome to React
We'll be using the create-react-appgenerator for this tutorial. To use the generator as well as run the React application server, you'll need Node.js JavaScript runtime and npm (Node.js package manager) installed. npm is included with Node.js which you can download and install from Node.js downloads.
Tip: To test that you have Node.js and npm correctly installed on your machine, you can type node --version and npm --version in a terminal or command prompt.
You can now create a new React application by typing:
where my-app is the name of the folder for your application. This may take a few minutes to create the React application and install its dependencies.
Note: If you've previously installed create-react-app globally via npm install -g create-react-app, we recommend you uninstall the package using npm uninstall -g create-react-app to ensure that npx always uses the latest version.
Let's quickly run our React application by navigating to the new folder and typing npm start to start the web server and open the application in a browser:
You should see the React logo and a link to 'Learn React' on http://localhost:3000 in your browser. We'll leave the web server running while we look at the application with VS Code.
To open your React application in VS Code, open another terminal or command prompt window, navigate to the my-app folder and type code .:
Markdown preview
In the File Explorer, one file you'll see is the application README.md Markdown file. This has lots of great information about the application and React in general. A nice way to review the README is by using the VS Code Markdown Preview. You can open the preview in either the current editor group (Markdown: Open Preview⇧⌘V (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+V)) or in a new editor group to the side (Markdown: Open Preview to the Side⌘K V (Windows, Linux Ctrl+K V)). You'll get nice formatting, hyperlink navigation to headers, and syntax highlighting in code blocks.
Syntax highlighting and bracket matching
Now expand the src folder and select the index.js file. You'll notice that VS Code has syntax highlighting for the various source code elements and, if you put the cursor on a parenthesis, the matching bracket is also selected.
IntelliSense
As you start typing in index.js, you'll see smart suggestions or completions.
After you select a suggestion and type ., you see the types and methods on the object through IntelliSense.
VS Code uses the TypeScript language service for its JavaScript code intelligence and it has a feature called Automatic Type Acquisition (ATA). ATA pulls down the npm Type Declaration files (*.d.ts) for the npm modules referenced in the package.json.
If you select a method, you'll also get parameter help:
Go to Definition, Peek definition
Through the TypeScript language service, VS Code can also provide type definition information in the editor through Go to Definition (F12) or Peek Definition (⌥F12 (Windows Alt+F12, Linux Ctrl+Shift+F10)). Put the cursor over the App, right click and select Peek Definition. A Peek window will open showing the App definition from App.js.
Press Escape to close the Peek window.
Hello World!
Let's update the sample application to 'Hello World!'. Create a new H1 header with 'Hello, world!' and replace the <App /> tag in ReactDOM.render with element.
Once you save the index.js file, the running instance of the server will update the web page and you'll see 'Hello World!' when you refresh your browser.
Tip: VS Code supports Auto Save, which by default saves your files after a delay. Check the Auto Save option in the File menu to turn on Auto Save or directly configure the files.autoSave user setting.
Debugging React
To debug the client side React code, we'll need to install the Debugger for Chrome extension.
Note: This tutorial assumes you have the Chrome browser installed. There are also debugger extensions for the Edge and Firefox browsers.
Open the Extensions view (⇧⌘X (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X)) and type 'chrome' in the search box. You'll see several extensions which reference Chrome.
Press the Install button for Debugger for Chrome.
Set a breakpoint
To set a breakpoint in index.js, click on the gutter to the left of the line numbers. This will set a breakpoint which will be visible as a red circle.
Npm In Visual Studio
Configure the Chrome debugger
We need to initially configure the debugger. To do so, go to the Run view (⇧⌘D (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+D)) and click create a launch.json file to customize Run and Debug. Choose Chrome from the Select Environment dropdown list. This will create a launch.json file in a new .vscode folder in your project which includes a configuration to launch the website.
We need to make one change for our example: change the port of the url from 8080 to 3000. Your launch.json should look like this:
Ensure that your development server is running (npm start). Then press F5 or the green arrow to launch the debugger and open a new browser instance. The source code where the breakpoint is set runs on startup before the debugger was attached, so we won't hit the breakpoint until we refresh the web page. Refresh the page and you should hit your breakpoint.
You can step through your source code (F10), inspect variables such as element, and see the call stack of the client side React application.
The Debugger for Chrome extension README has lots of information on other configurations, working with sourcemaps, and troubleshooting. You can review it directly within VS Code from the Extensions view by clicking on the extension item and opening the Details view.
Live editing and debugging
If you are using webpack together with your React app, you can have a more efficient workflow by taking advantage of webpack's HMR mechanism which enables you to have live editing and debugging directly from VS Code. You can learn more in this Live edit and debug your React apps directly from VS Code blog post and the webpack Hot Module Replacement documentation.
Linting
Linters analyze your source code and can warn you about potential problems before you run your application. The JavaScript language services included with VS Code has syntax error checking support by default, which you can see in action in the Problems panel (View > Problems⇧⌘M (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+M)).
Try making a small error in your React source code and you'll see a red squiggle and an error in the Problems panel.
Linters can provide more sophisticated analysis, enforcing coding conventions and detecting anti-patterns. A popular JavaScript linter is ESLint. ESLint, when combined with the ESLint VS Code extension, provides a great in-product linting experience.
First, install the ESLint command-line tool:
Then install the ESLint extension by going to the Extensions view and typing 'eslint'.
Once the ESLint extension is installed and VS Code reloaded, you'll want to create an ESLint configuration file, .eslintrc.js. You can create one using the extension's ESLint: Create ESLint configuration command from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)).
The command will prompt you to answer a series of questions in the Terminal panel. Take the defaults, and it will create a .eslintrc.js file in your project root that looks something like this:
ESLint will now analyze open files and shows a warning in index.js about 'App' being defined but never used.
You can modify the ESLint rules in the .eslintrc.js file.
Let's add an error rule for extra semi-colons:
Now when you mistakenly have multiple semicolons on a line, you'll see an error (red squiggle) in the editor and error entry in the Problems panel.
Popular Starter Kits
In this tutorial, we used the create-react-app generator to create a simple React application. There are lots of great samples and starter kits available to help build your first React application.
VS Code React Sample
This is a sample React application used for a demo at the 2016 //Build conference. The sample creates a simple TODO application and includes the source code for a Node.js Express server. It also shows how to use the Babel ES6 transpiler and then use webpack to bundle the site assets.
Npm In Visual Studio Code
TypeScript React
If you're curious about TypeScript and React, you can also create a TypeScript version of the create-react-app application by specifying that you want to use the TypeScript template:
See the details at Adding TypeScript on the Create React App site.
Angular
Angular is another popular web framework. If you'd like to see an example of Angular working with VS Code, check out the Chrome Debugging with Angular CLI recipe. It will walk you through creating an Angular application and configuring the launch.json file for the Debugger for Chrome extension.
Common questions
How To Run Npm In Visual Studio
Can I get IntelliSense within declarative JSX?
Npm In Visual Studio 2015
Yes. For example, if you open the create-react-app project's App.js file, you can see IntelliSense within the React JSX in the render() method.
